Acalvio Threat Research Labs.
Introduction
Emotet is one of many information stealer malware families which have been active in the recent months. The initial delivery vector of the malware is via phishing campaign. The blog by TrendMicro[1] and Microsoft[2] discusses the first stage infection of the malware and shares statistics on the global infection. Once a corporation has been infected with Emotet, it can spread throughout the internal network. In this blog we detail the lateral movement technique which have been employed by the malware and its detection by a deception-based architecture.
Lateral Movement :
Once it has enumerated the resources, it calls the function WNetAddConnection2. The WNetAddConnection2 function makes a connection to a network resource and can redirect a local device to the network resource. The second and the third parameter of the function WNetAddConnection2 requires the username and passwords.
If lpUserName is NULL, the function uses the default username. The user context for the process provides the default username. If the password is NULL, the function uses the current default password associated with the user specified by the lpUserName parameter. By specifying these parameters as NULL, Emotet makes uses of username and password of the current user to connect to the resources. This methodology is the same as that employed by many families of ransomware for infecting unmapped drives.
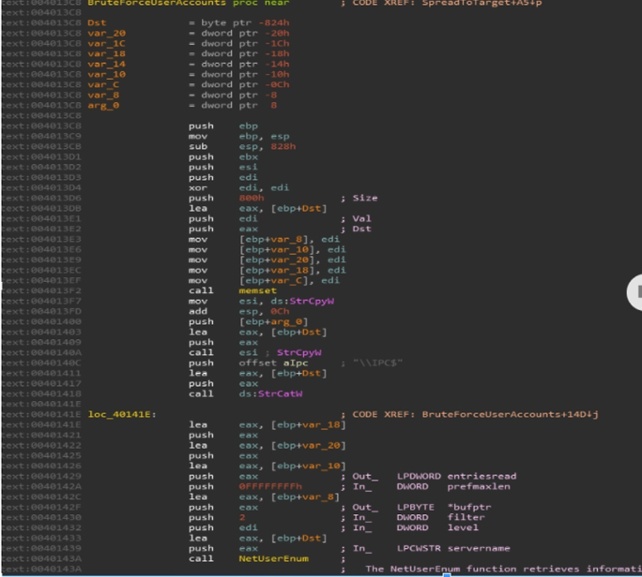
As a second method to spread inside the compromised network, Emotet makes the call to NetUserEnum API. The server name value passed to the NetUserEnum function is appended with “//IPC$,” which it gets it from the NETRESOURCE structure from the earlier call to WNetEnumResourceW. The function NetUserEnum returns all the usernames which are active on a server.
Once it has retrieved the list of username, Emotet, as shown in figure 4.0, connects to the target $IPC share by brute forcing passwords. The list of the brute force password is available here.
If the first two methods fail to authenticate, Emotet will attempt a brute force of the user “Administrator” with the same password list as used in method 2.
Once it has been able to connect to the server, it makes a copy of itself on the target computer.
After copying itself to the target computer, it opens service manager and creates a service with API call CreateServiceW, using the copied file as a parameter. StartServiceA is then made to is to execute the malicious file.
Detection by Deception:
Detection of emotet involves projecting honey unmapped drives. Network enumeration will generate SMB request to the unmapped drives leading to its instant detection. Below is the screenshot of the detection in the ShadowPlex.
When the files gets copied to the unmapped drives, it will lead to the engagement of the Emotet malware and will trigger the process to isolation the infected endpoint from the network.
Conclusion :
Lateral movement and spreading inside the network is one of the widely and commonly used techniques by threat actors. Emotet not only enumerates and tries to access the drives by using the username and password of the infected user, but also gets the username which is active on a server and then brute forces the passwords.
A deception centric architecture is a robust architecture to not only detect the infection but also diverts the threat to the engagement platform for the generation of IoC’s. These IoC’s can then be used to quarantine the infected machines and can be used to label the threat actor.
IoC of the analyzed file :
- 8d8b45aa8724458ea7711f13ee237bbd3e4c77669ebd91109b94620ecc52bc72
References
[1]EMOTET Returns, Starts Spreading via Spam Botnet
[2] Mitigating and eliminating info-stealing Qakbot and Emotet in corporate networks


